Linux 기초 실습 07 PROCESS
Linux Lecture Practice 07 PROCESS
Introduction
이번 실습에서는 프로세스 조작하기 실습과 셸의 대해 알아보겠습니다.
getpid(), getppid()
- pid_t pid = getpid()
getppid() - pid_t는 프로세스 번호를 지칭(사실 int 값)
- getpid() : 현재 프로세스의 번호를 가져옴
- getppid() : 부모 프로세스의 번호를 가져옴
getpid(), getppid() 실습 (getpid.c 작성)
#include <unistd.h>
#include <stdio.h>
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
pid_t pid, ppid;
pid = getpid();
ppid = getppid();
printf("PID : %d, PPID : %d\n", pid, ppid);
return 0;
}
getpid(), getppid() 실습
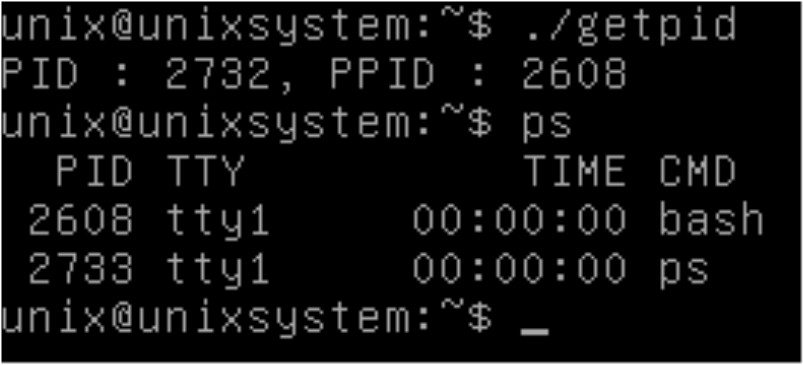
bash가 getpid의 부모 프로세스
fork()
- pid_t pid = fork()
- 프로세스 이미지를 복제
- 복제 당시의 프로세스 이미지는 같음
- 리턴 값
- 부모 프로세스 : 자식 프로세스 ID(> 0)
- 자식 프로세스 : 0
- 오류 : -1
fork() 실습 (fork.c 작성)
#include <unistd.h>
#include <stdio.h>
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
pid_t pid;
printf("Calling fork()\n");
pid = fork();
if(pid > 0)
printf("Parent PIDs : %d, %d, %d\n", pid, getpid(), getppid());
else if(pid == 0)
printf("Child PIDs : %d, %d, %d\n", pid, getpid(), getppid());
else
printf("fork() error.\n");
return 0;
}
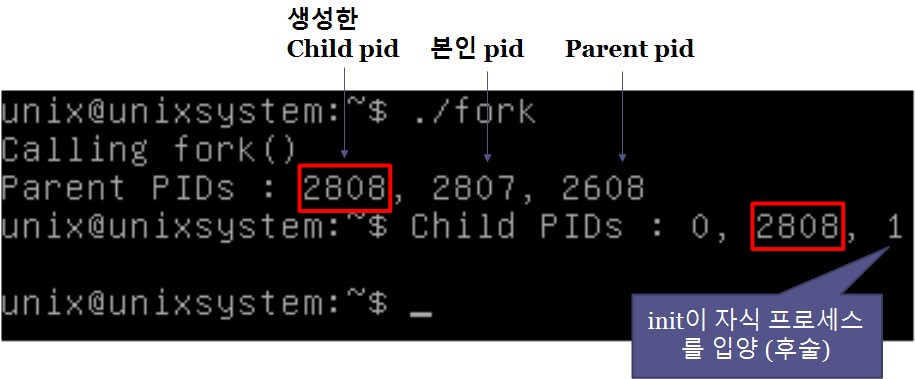
exec() 계열
exec() 계열 (1/4)
- execve(const char *filename, char *const argv[], char *const envp[])
- filename : 실행할 파일의 이름 (프로세스)
- argv : 실행할 파일의 인자 값
- envp : 프로세스에서 사용할 환경 변수
- 오류가 생기면 반환 값이 있음
- 실행이 완료되면 반환 값이 없음 (이미지 자체가 변경)
exec() 계열 (2/4)
- execl(path, arg0, arg1, …)
- execv(path, argv[])
- execle(path, arg0, arg1, …, envp[])
- execve(path, argv[], envp[])
- execlp(file, arg0, arg1, …)
- execvp(file, argv[])
exec() 계열 (3/4)
- 인자를 여러 개의 변수로 받는 경우
- execl(path, arg0, arg1, …)
- execle(path, arg0, arg1, …, envp[])
- execlp(file, arg0, arg1, …)
- 인자를 하나의 벡터로 받는 경우
- execv(path, argv[])
- execve(path, argv[], envp[])
- execvp(file, argv[])
- 마지막 인자는 반드시 NULL로 끝내야 함
exec() 계열 (4/4)
- 환경변수를 따로 받는 경우
- execle(path, arg0, arg1, …, envp[])
- execve(path, argv[], envp[])
- PATH 변수를 자동으로 검색하는 경우
- execlp(file, arg0, arg1, …)
- execvp(file, argv[])
- ‘/’ 기호가 없으면 PATH를 통해 파일을 검색
- PATH의 기본 값은 ‘/bin:/usr/bin’
exec() 계열 실습 (exec.c 작성)
#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
pid_t pid;
if(argc > 1)
{
pid = fork();
if(pid == 0)
{
execl(argv[0], argv[0], NULL);
perror("execl() failed.\n");
}
else
{
printf("%s is running as parent.\n", argv[0]);
return 0;
}
}
else
printf("%s is running alone.\n", argv[0]);
return 0;
}
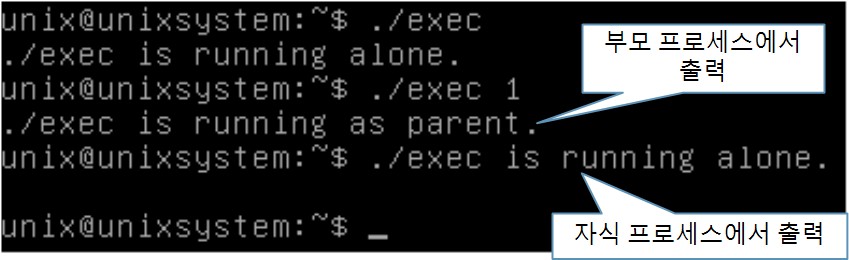
sleep(), wait(), waitpid()
sleep(), wait(), waitpid() (1/2)
- sleep(int seconds)
<unistd.h>- 지정된 시간(초 단위)만큼 일시 정지
- wait(int* status)
<sys/wait.h>- 임의의 자식 프로세스가 종료되기를 기다림
- 반환 값은 먼저 종료된 자식 프로세스의 ID
- 상태 값은 자식 프로세스의 반환 값
sleep(), wait(), waitpid() (2/2)
- waitpid(pid_t child, int* status, int options)
<sys/types.h>,<sys/wait.h>- child로 지정된 프로세스가 종료되기를 기다림
- -1 : 임의의 자식 프로세스
- 0 : 프로세스 그룹이 같은 자식 프로세스
- > 0 : 프로세스 ID가 같은 자식 프로세스
- < -1 : 프로세스 그룹이 절댓값과 같은 자식 프로세스
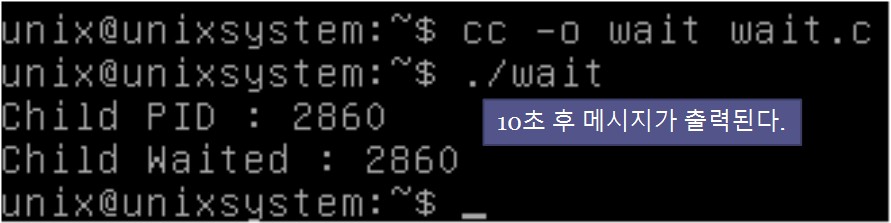
sleep(), wait() 실습 (wait.c 작성)
#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/wait.h>
int main() {
pid_t pid;
pid = fork();
if(pid == 0) {
sleep(10); // sleep for 10 sec.
}
else {
printf("Child PID : %d\n", pid);
pid = wait(NULL);
printf("Child Waited : %d\n", pid);
}
return 0;
}
고아 프로세스와 좀비 프로세스
고아 프로세스(Orphan Process)
- 부모 프로세스가 먼저 종료
- init(1) 프로세스가 자동으로 프로세스를 ‘입양’
- 데몬(daemon) 등의 동작을 가능케 함
데몬(daemon)
사용자가 직접적으로 제어하지 않고,
백그라운드에서 돌면서 여러 작업을 하는 프로그램
(부모 프로세스가 PID 1(init)이고 제어하는 terminal이 없을 때,
그 프로세스를 daemon이라 한다)
좀비 프로세스(Zombie Process)
- 자식 프로세스가 먼저 종료
- 부모 프로세스는 자식 프로세스의 종료 여부를 확인하지 못함
- 자식 프로세스의 이미지가 회수되지 못함 (좀비 상태)
고아 프로세스 실습 (orphan.c 작성)
#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/wait.h>
int main() {
pid_t pid;
pid = fork();
if(pid == 0)
sleep(60);
else
printf("Child will terminate in 60 secs.\n");
return 0;
}
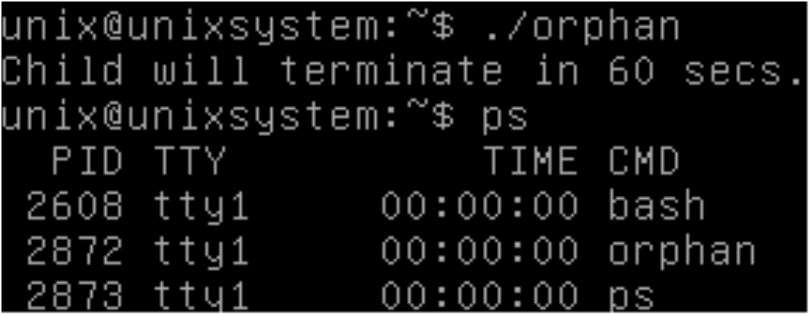
orphan 프로세스는 아직 살아 있음
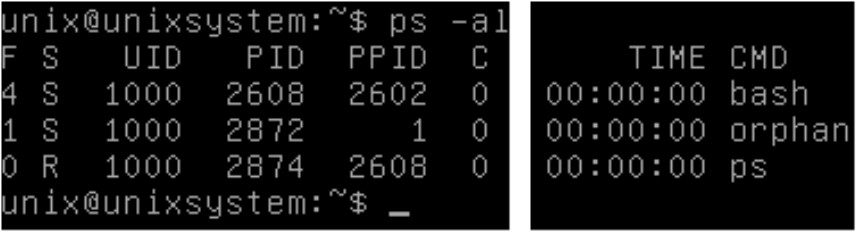
init(1) 프로세스가 orphan 프로세스를 입양하였다.
(프로세스는 60초 후 자동 종료)
Option
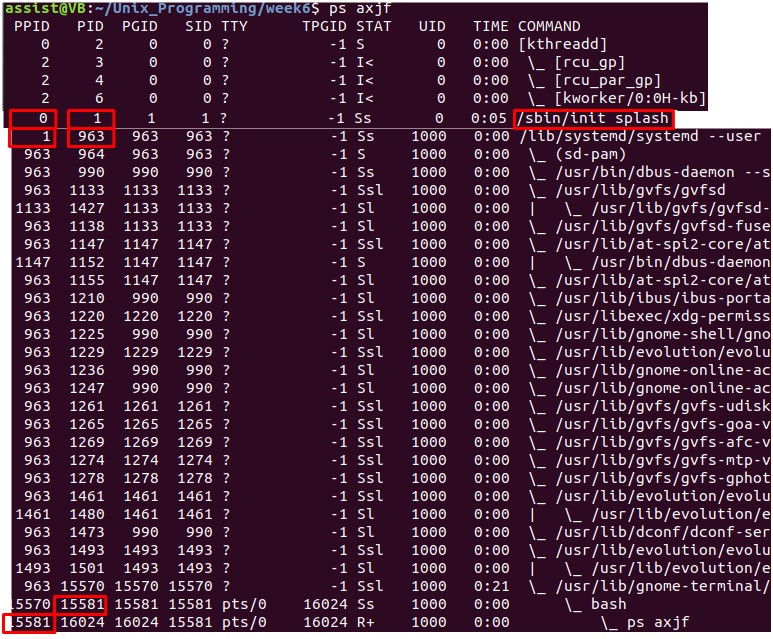
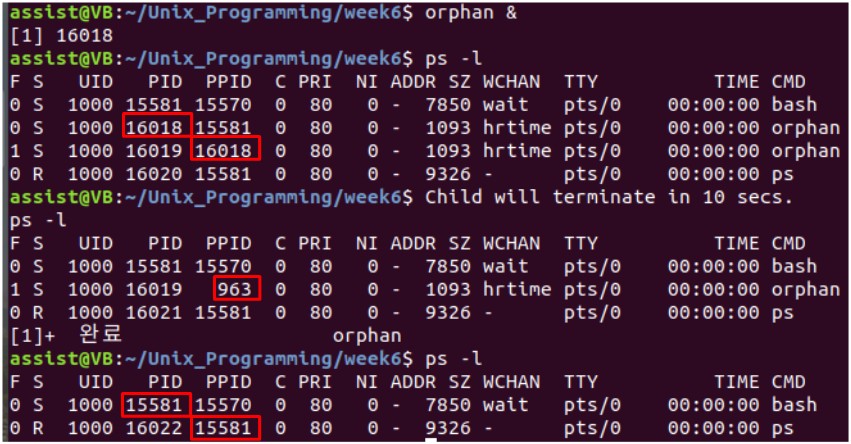 orphan process를 입양하는 process의 PID가 1이 아니다?
orphan process를 입양하는 process의 PID가 1이 아니다?
Who is 963?
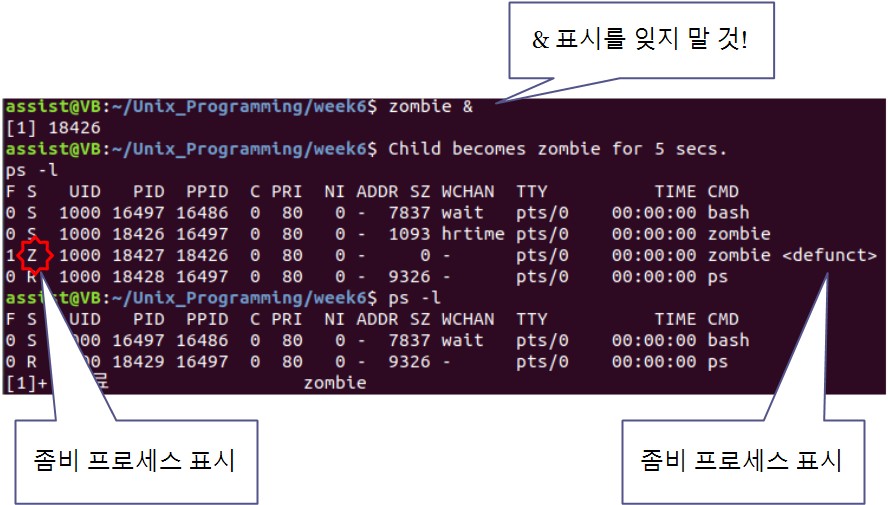
좀비 프로세스 실습 (zombie.c 작성)
#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/wait.h>
int main
{
pid_t pid;
pid = fork();
if(pid != 0) // Parent
sleep(5);
else // Child or error
printf("Child becomes zombie for 5 secs. \n");
return 0;
}
좀비 프로세스 실습
셸(Shell)?
- 입력하는 명령을 해석하여 수행시키는 프로그램
-
로그인을 할 때마다 반드시 셸로 진입
- 셸의 종류
- Bourne Shell (sh), Bourne Again Shell (bash) : $
- C Shell (csh) : %
- KornShell (ksh) : $
셸의 기본 처리 과정
- 사용자의 입력을 받는다.
- exec()에 적합한 형태로 사용자 입력을 재구성한다.
- fork()를 통해 처리할 프로세스를 생성한다.
- exec()를 통해 자식 프로세스를 수행한다.
- wait()를 통해 부모 프로세스가 대기한다.
- 위의 과정을 로그아웃 까지 반복 수행
마무리
이상으로 이번 실습을 마치겠습니다.
열심히 따라와 주셔서 감사합니다!
댓글남기기